Computers are incredible machines that can accomplish practically anything, but they are not without flaws. They occasionally face faults that cause them to act oddly or to cease operating entirely. These mistakes can be aggravating and perplexing, especially if you don’t understand what they signify or how to correct them. But don’t panic; you don’t have to throw away your computer or reinstall your operating system every time an error message appears.
Beep Codes: What Your Computer Is Trying to Tell You
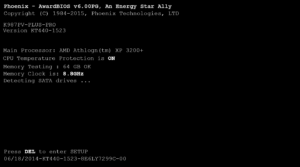
When you power on your computer, you may hear a beep sound, indicating that it is doing a self-test. This is known as the POST (Power-on self-test), and it checks to see if all of your computer’s important components are functioning properly. If everything is in order, you will hear one or two beeps (depending on the brand of your motherboard) and your computer will boot normally. If there is a problem, you will hear more than two beeps and your computer may not boot at all. These are known as beep codes, and they change depending on the manufacturer and BIOS version. Beep codes allow your computer to communicate with you and inform you of any problems.
It might be anything from a malfunctioning graphics card to a dead battery. You may find out what each beep code represents by consulting your motherboard’s handbook or searching online.
Blue Screen of Death: The Dreaded Error That Stops Everything
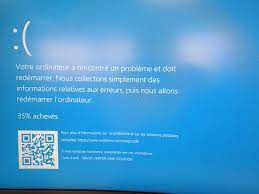
The Blue Screen of Death, or BSOD, is one of the most well-known and dreaded mistakes that may occur to any Windows user. This occurs when your computer unexpectedly fails and displays a blue screen with technical details and an error code. This error is typically caused by a hardware or software issue that causes your system to become unstable and unable to function. It might be the result of a recent modification to your computer, such as installing a new device or program, or it could be the result of a virus or malware infestation. When you get a BSOD, the best thing to do is restart your computer and try to reverse the change that caused it. You may also use applications like Nirsoft BlueScreenView, WhoCrashed, or Reliability Monitor to analyze the dump files and logs created by your computer when it crashes and determine the root cause.
Out of Memory: When Your Computer Runs Out of Space

Out of Memory is another typical mistake that you may encounter when using your computer. This issue happens when your computer lacks sufficient RAM (Random Access Memory) or virtual memory to operate all of the apps that you wish to utilize. RAM is the temporary memory that your computer utilizes while it is operating to store and process data. When your computer runs out of physical memory, it uses virtual memory on your hard drive as an expansion of RAM. To resolve this problem, you must either update your RAM by purchasing additional memory chips or increase the capacity of your virtual memory by adjusting various system settings.
To increase the size of your virtual memory, follow these steps:
- Open the Control Panel and navigate to System and Security > System > Advanced system settings.
- Select the Advanced tab, then select Settings under Performance.
- Return to the Advanced tab and choose Change under Virtual memory.
- Uncheck the Automatically manage paging file size for all disks box.
- Choose the drive where Windows is installed, then choose Custom size.
- Enter a number for the virtual memory’s starting and maximum sizes in megabytes. It is advised that your virtual memory be 1.5 to 2 times the capacity of your RAM.
- Select Set, followed by OK.
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.
Missing DLL: When Your Computer Can’t Find What It Needs
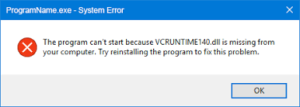
When you attempt to execute an application, you may receive an error message stating that a DLL file is missing or not found. DLL is an abbreviation for Dynamic Link Library, which is a file containing code and data that may be utilized by different programs. Some programs require specific DLL files to work properly; however, if such files are destroyed, damaged, or relocated, the program will fail to locate them and will display an error message. To resolve this issue, you must either reinstall the software that caused the error or obtain a copy of the missing DLL file from a reputable web source. However, avoid downloading DLL files from unfamiliar websites since they may include viruses.
Device Manager: How to Troubleshoot Your Hardware Problems
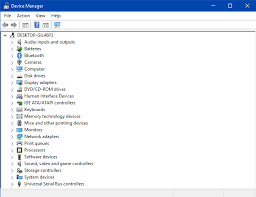
If one of your devices, such as your printer, scanner, keyboard, or mouse, stops operating correctly, you may need to check the Device Manager to see what is wrong. The Device Manager is a program that displays all of the devices that are connected to your computer as well as their status. The Device Manager may be accessed by entering devmgmt.msc into the Start menu or by heading to Control Panel > Hardware and Sound > Device Manager. You can check whether any of your devices have a yellow exclamation mark or a red cross next to them in the Device Manager, indicating that they have a problem. To discover additional information about the problem and the error code, right-click on the device and select Properties. You may also try to update the device’s driver by clicking Update Driver, or you can remove and reinstall the device by selecting remove and then Scan for hardware changes. If these procedures do not work, you can look up the problem number and locate a solution online.
Unhandled Exception: When Your Program Crashes Unexpectedly
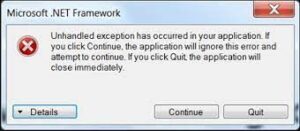
When running a software, it may occasionally cease operating and display an error message stating that an unhandled exception has occurred. This indicates that the program met an unexpected scenario that it was unable to manage and was forced to terminate. This might be due to a program problem, a conflict with another program, or a lack of system resources. To resolve this problem, restart the software and check if it works again. You can also check for program updates or contact the developer for assistance. If the issue continues, search for the error code to learn what it implies and how to fix it.
Error Codes: What They Mean and How to Decode Them
When your computer or application displays an error message, it generally includes an error code, which is a number or a combination of characters and digits. These error codes are intended to assist you in determining the kind and source of the issue and locating a solution. These error codes, however, are not always simple to comprehend or remember, especially if they are long or complex. Fortunately, there are various methods for decoding these error codes and determining what they imply.

One way is to utilize Microsoft’s help site, which has a list of all the error codes used by Windows and other Microsoft products, as well as what they indicate. Error 22, for example, signifies ERROR_BAD_COMMAND, which means the command you typed is unknown to the software. Error 225 (0xE1) denotes ERROR_VIRUS_INFECTED, which indicates that the file is infected with a virus or malware.
Another way is to use Google or another search engine to look for the error number and obtain relevant information from a variety of sources, such as forums, blogs, publications, and so on. You may also utilize internet programs to translate error codes into plain English, such as Err.exe or Error Lookup Tool.
Web Errors: How to Deal with Browser Issues
While surfing the web, you may come across several issues that restrict you from visiting specific websites or reading specific material. Problems with the web server, your browser, or your internet connection are frequently at blame for these issues. The following are some of the most typical online errors:
- 404 Not Found: This indicates that the requested web page does not exist on the server. This might be due to the page being removed, relocated, or mistyped. Check if you typed the proper URL or attempt to locate another link to the website to resolve this problem.
- 408 Request Timeout: This indicates that your browser did not get a response from the server within a specified time frame. This might be due to a sluggish internet connection, a busy server, or a firewall preventing your request from being processed. Refresh the page or try again later to resolve this issue.

- 403 Forbidden: This indicates that you do not have authorization to visit the requested web page. This might be due to the fact that you need to check in with a username and password, or the page is blocked for some reason. Look for authentication details or contact the website’s owner to resolve this problem.
- 400 Bad Request: This indicates that your browser attempted to send an invalid request to the server. This might be because your browser is out of date or incompatible with the web page, or you need to install plugins or extensions to read the content. To resolve this issue, upgrade your browser or install the necessary plugins.
- 406 Not Acceptable: This signifies that your browser is unable to show the web page’s content because it does not support its format or language. This might be because your browser lacks the required software or settings to display the information. Download the necessary software or update your browser settings to resolve this issue.
These are some of the most typical computer mistakes you could experience when using your computer or surfing the web. We hope this post has helped you understand what these problems signify and how to quickly correct them. If you have any questions or comments, please leave them in the comments section.











+ There are no comments
Add yours